-
Original Article
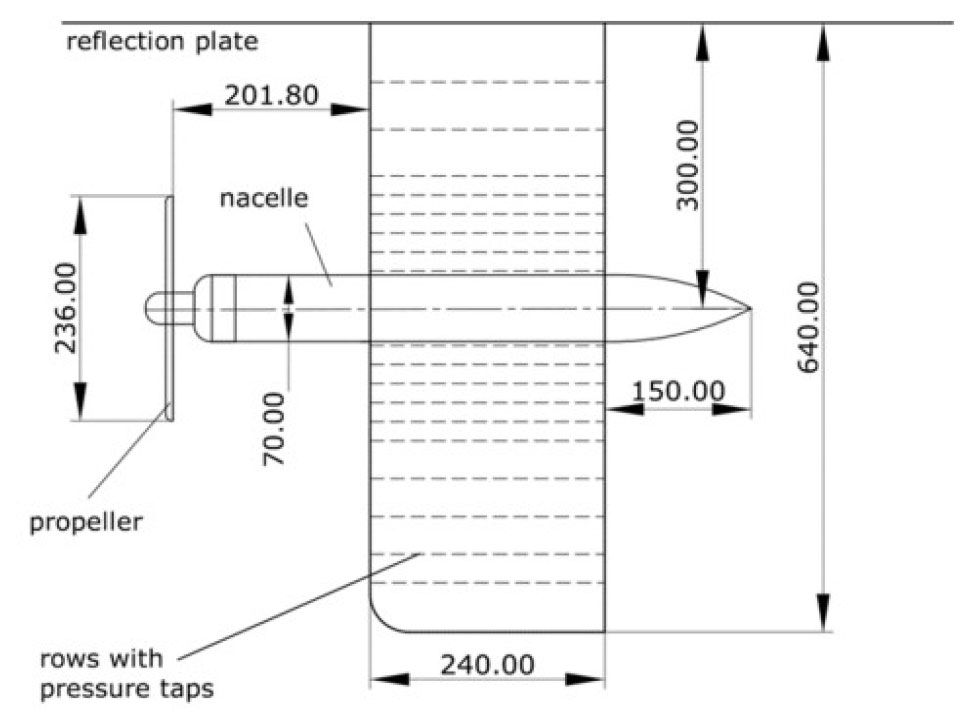
-
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF AERODYNAMIC AND ACOUSTIC PERFORMANCE BETWEEN DISTRIBUTED ELECTRIC PROPULSION AND EQUIVALENT SINGLE PROPELLER
분산전기추진시스템과 등가 단일 프로펠러 간의 공력 및 소음 성능 비교 연구
-
H.S. Song, Y.H. Hwang, R.S. Myong, H. Lee
송현수, 황유현, 명노신, 이학진
- Distributed electric propulsion(DEP) has attracted attention as a sustainable alternative to conventional propulsion systems in pursuit of carbon-neutral aviation. Although DEP systems …
- Distributed electric propulsion(DEP) has attracted attention as a sustainable alternative to conventional propulsion systems in pursuit of carbon-neutral aviation. Although DEP systems offer advantages such as improved aerodynamic control and reduced noise emissions, the complex flow interactions among multiple rotors and the wing surface should be investigated to ensure reliable performance prediction. This study presents a comparative numerical analysis of aerodynamic and acoustic performance between a single-propeller configuration and a DEP system under equivalent thrust and tip Mach number conditions. Flow simulations were conducted using the Lattice Boltzmann Method(LBM), and far-field acoustic predictions were obtained via the Ffowcs Williams-Hawkings(FW-H) method under impermeable surface assumptions. The DEP configuration with three propellers generated a more spanwise-uniform suction distribution, yielding a 5-8% increase in lift coefficient compared to the single-propeller case. However, drag was slightly higher due to increased friction from multiple rotors. Moreover, the DEP system achieved an average noise reduction of 2-3 dB in Overall Sound Pressure Level(OASPL), with a maximum reduction of 4.1 dB observed in the downward direction. These results demonstrate that DEP systems can offer aerodynamic benefits while significantly reducing noise emissions, supporting their applicability to next generation low noise air vehicle designs. - COLLAPSE
-
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF AERODYNAMIC AND ACOUSTIC PERFORMANCE BETWEEN DISTRIBUTED ELECTRIC PROPULSION AND EQUIVALENT SINGLE PROPELLER
-
Original Article
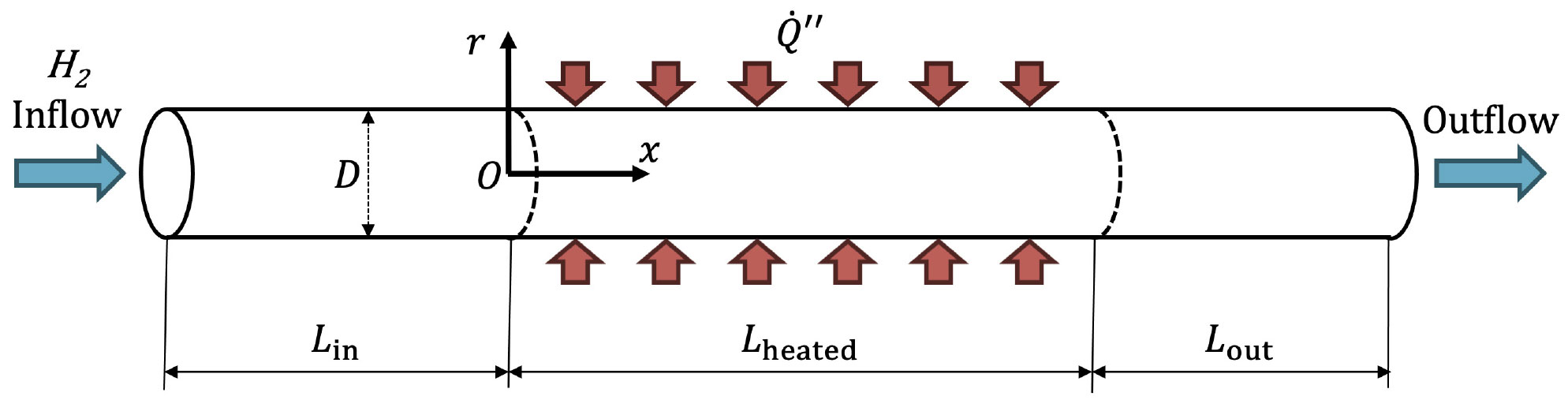
-
VALIDATION AND EVALUATION OF KNOPP ROUGHNESS MODELING FOR TURBULENT FLOW AND HEAT TRANSFER UNDER VARYING ROUGHNESS REGIMES
다양한 거칠기 구간에서의 난류 유동 및 열전달에 대한 Knopp 거칠기 모델의 검증 및 평가
-
S. Jeong, S. Han, B.J. Lee
정석현, 한서음, 이복직
- Accurate modeling of surface roughness effects is critical for predicting turbulent flow and heat transfer characteristics in practical engineering systems. This study …
- Accurate modeling of surface roughness effects is critical for predicting turbulent flow and heat transfer characteristics in practical engineering systems. This study investigates the performance and applicability of the Knopp roughness model coupled with the k - ω SST turbulence model implemented in CRUNCH CFD, validated against two benchmark experimental datasets: the incompressible turbulent pipe flow experiments by Nikuradse and the transcritical heat transfer experiments in supercritical hydrogen flow by Niino. To comprehensively assess the model’s predictive capability, two different near-wall treatment strategies, the wall-function approach and the wall-resolved approach, were systematically applied and compared. For the Nikuradse cases, the wall-function approach demonstrated stable and accurate predictions of velocity profiles and friction factors across hydraulically smooth to fully rough regimes. Conversely, the wall-resolved approach exhibited high accuracy in smooth and fully rough conditions but encountered increased deviations in the transitionally rough regime, attributed to the model’s inherent reliance on the single nondimensional roughness parameter ( k s + ), thus lacking sensitivity to Reynolds number variations. In the Niino cases involving supercritical hydrogen flows, characterized by significant near-wall property gradients and thermal spikes, the wall-resolved approach consistently yielded accurate predictions of thermal behavior and pressure drop, whereas the wall-function approach showed limitations in accurately capturing thermal spike phenomena under high heat flux conditions. The findings highlight the effectiveness of the Knopp model combined with wall-resolved methods for complex, thermally sensitive conditions, while suggesting further model improvements incorporating additional flow variables to enhance predictions in transitionally rough regimes. - COLLAPSE
-
VALIDATION AND EVALUATION OF KNOPP ROUGHNESS MODELING FOR TURBULENT FLOW AND HEAT TRANSFER UNDER VARYING ROUGHNESS REGIMES
-
Original Article
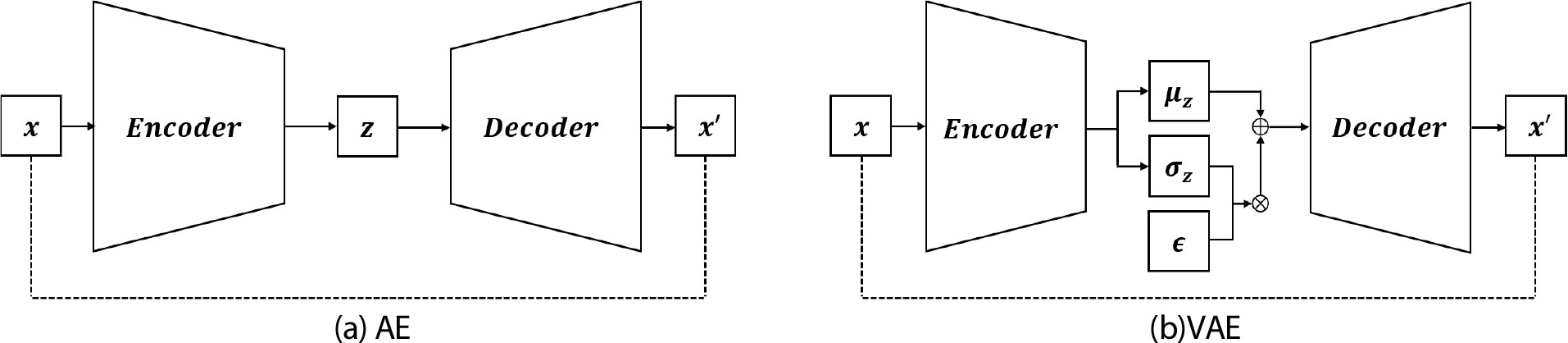
-
VARIATIONAL AUTOENCODER BASED REDESIGNING DESIGN SPACES FOR EFFICIENT MISSILE GEOMETRY DESIGN
미사일 형상 설계 효율화를 위한 변이형 오토인코더 기반 설계 공간 재설정
-
J. Shin, K. You, Y. Kang, S. Jeong, J. Choi, S. Lee
신종현, 유강국, 강유업, 정신규, 최종원, 이상아
- Aerodynamic shape optimization is often hindered by high-dimensional design spaces containing large infeasible regions, which complicates the search for optimal solutions. This …
- Aerodynamic shape optimization is often hindered by high-dimensional design spaces containing large infeasible regions, which complicates the search for optimal solutions. This study proposes a methodology to redesign the design space for 3D missile geometry using a variational autoencoder (VAE) to overcome these challenges. A continuous, low-dimensional latent space that implicitly embeds the complex feasibility constraints is learned by training a VAE exclusively on a dataset of feasible shapes. The results demonstrate that this redesigned space significantly improves the generation rate of feasible designs compared to the original space. This study concludes that redesigning the design space with a VAE is a promising strategy to enhance the efficiency and stability of 3D shape optimization by transforming a complex, constrained problem into a more tractable, unconstrained alternative. - COLLAPSE
-
VARIATIONAL AUTOENCODER BASED REDESIGNING DESIGN SPACES FOR EFFICIENT MISSILE GEOMETRY DESIGN
-
Original Article
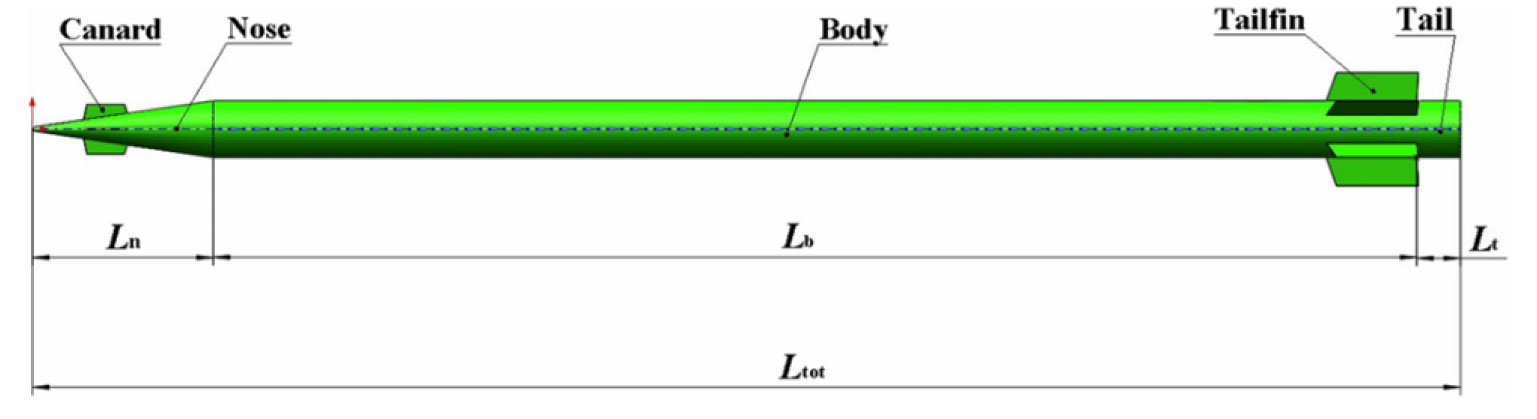
-
VALIDATION OF A SEMI-EMPIRICAL CODE FOR ROCKET AERODYNAMIC PERFORMANCE PREDICTION AND MULTI-OBJECTIVE OPTIMIZATION
로켓 공력 성능 예측을 위한 반경험식 코드 검증 및 다목적 최적화
-
D.M. Joo, M.K. Kim, S.M. Park, N.Y. Lee, H. Kim
주동묵, 김민경, 박성민, 이나영, 김형진
- This study verifies accuracy of a semi-empirical (SEM) code for predicting the aerodynamic performance of rockets. The reliability of the SEM code …
- This study verifies accuracy of a semi-empirical (SEM) code for predicting the aerodynamic performance of rockets. The reliability of the SEM code was established by cross- validating its results with those from CFD simulations and Missile DATCOM. Subsequently, the NSGA-II evolutionary algorithm was applied to perform a multi-objective optimization considering both the lift-to-drag ratio and static margin for a wide range of freestream Mach numbers. As a result, the optimized configuration demonstrated improvements in both performance metrics, thereby validating the efficiency and practicality of the semi-empirical design approach as a tool for early-stage conceptual design of rockets in high-speed flow environments. - COLLAPSE
-
VALIDATION OF A SEMI-EMPIRICAL CODE FOR ROCKET AERODYNAMIC PERFORMANCE PREDICTION AND MULTI-OBJECTIVE OPTIMIZATION
-
Original Article
-
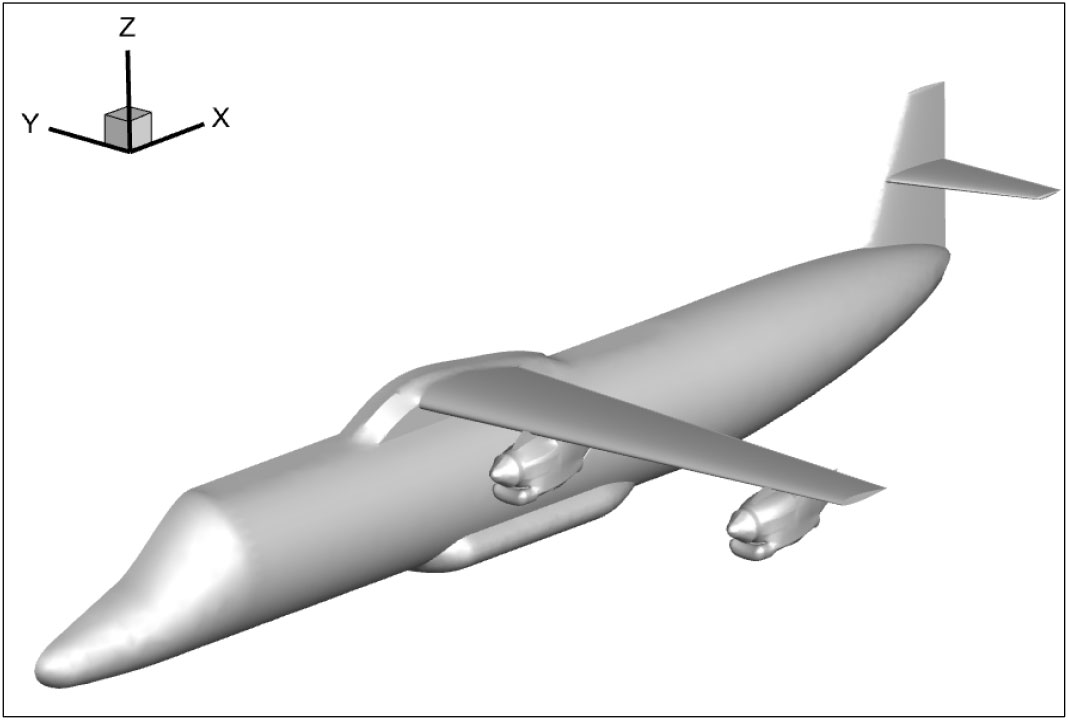
EFFECTS OF NACELLE SPANWISE POSITION ON AERODYNAMIC PERFORMANCE OF A PART23 HYDROGEN FUEL CELL COMMUTER AIRCRAFT
Part 23 급 수소연료전지 커뮤터기의 나셀의 스팬 방향 배치에 따른 공력 영향성 분석
-
B. Nabanita, G. Kim, S.H. Oh, R.S. Myong
나바니타브라마차리, 김건, 오승환, 명노신
- The implementation of multi-engine propulsion in next-generation hydrogen fuel cell aircraft introduces new challenges in aerodynamic integration, particularly concerning nacelle placement along …
- The implementation of multi-engine propulsion in next-generation hydrogen fuel cell aircraft introduces new challenges in aerodynamic integration, particularly concerning nacelle placement along the wing span. This study investigates the aerodynamic impact of varying nacelle spanwise positions through a comparative computational analysis. Five under-wing nacelle configurations were evaluated using Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) simulations, incorporating the Spalart-Allmaras turbulence model. Simulations were performed at a representative cruise condition with a freestream velocity of 110 m/s. Key aerodynamic parameters, lift coefficient, drag coefficient, and lift-to-drag ratio were assessed. The results reveal that nacelle positioning significantly influences aerodynamic performance, with overly inboard clustering degrading lift and wake structure, while moderately inboard or outboard placements offer improved flow symmetry and a lift-to-drag ratio ranging from 8.01 to 12.54, depending on nacelle placement. These findings provide valuable insights for early-stage design optimization in hydrogen aircraft propulsion systems, where aerodynamic efficiency must be balanced with structural and propulsion integration constraints. - COLLAPSE
-
EFFECTS OF NACELLE SPANWISE POSITION ON AERODYNAMIC PERFORMANCE OF A PART23 HYDROGEN FUEL CELL COMMUTER AIRCRAFT
-
Original Article

-
CFD-BASED CORRECTION METHOD FOR AERODYNAMIC PERFORMANCE IN ICED AIRFOIL WIND TUNNEL TESTING
전산유체역학을 활용한 착빙 익형 풍동시험의 공력 성능 보정 기법
-
D.H. Kim, J. Park, J. Jang, J. Kim, J.S. Park, S. Lee
김동현, 박진이, 장종윤, 김준, 박진석, 이승수
- This paper proposes an correction method for predicting the aerodynamics of iced airfoil in icing wind tunnel test. Because of endplate effect, …
- This paper proposes an correction method for predicting the aerodynamics of iced airfoil in icing wind tunnel test. Because of endplate effect, measuring the precise aerodynamics of a two-dimensional iced airfoil in wind tunnel is difficult. The proposed method synthesizes the aerodynamic characteristics of a iced wing with those of a clean wing in wind tunnel, to estimate the aerodynamics of iced airfoil. The method is validated by comparing its predictions with recent wind tunnel experiments. The results confirm that the simulated aerodynamics of the clean wing, including endplate effects, agree well with the experimental results before icing. And the synthesized aerodynamic changes due to icing show good agreement with the experimental results for the iced wing. - COLLAPSE
-
CFD-BASED CORRECTION METHOD FOR AERODYNAMIC PERFORMANCE IN ICED AIRFOIL WIND TUNNEL TESTING
-
Original Article
-
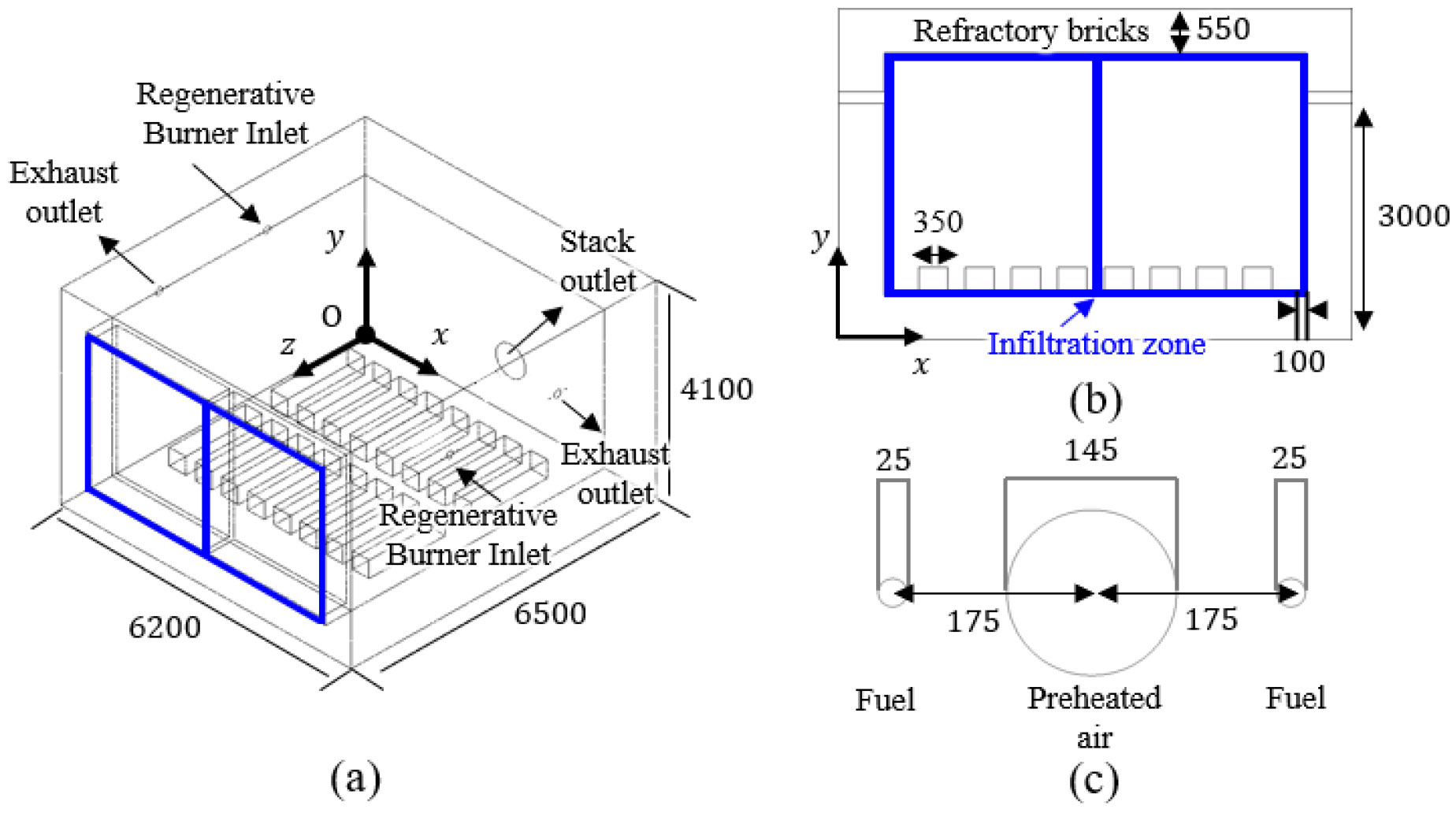
NUMERICAL STUDY ON THE THERMO-FLUID CHARACTERISTICS OF A REHEATING FURNACE WITH REGENERATIVE BURNER SWITCHING OPERATION
축열식 버너의 전환을 고려한 가열로 내부 열유동에 관한 수치적 연구
-
J. Kim, G. Son
김준엽, 손기헌
- In this study, the effects of regenerative burner switching operation on the thermo-fluid characteristics inside a reheating furnace are numerically investigated using …
- In this study, the effects of regenerative burner switching operation on the thermo-fluid characteristics inside a reheating furnace are numerically investigated using ANSYS Fluent. The combustion process is modeled with the Finite-Rate/Eddy-Dissipation (FR/ED) model, while radiative heat transfer is handled by the Discrete Ordinates (DO) model. The numerical model is first validated against benchmark data from previous studies to ensure its reliability. Subsequently, a parametric study is conducted to investigate the influence of stored heat variation and periodic burner switching on the internal thermo-fluid field. The results elucidate how these parameters affect flow and temperature distributions within the furnace and determine the characteristic time required for the system to reach a periodic steady state. - COLLAPSE
-
NUMERICAL STUDY ON THE THERMO-FLUID CHARACTERISTICS OF A REHEATING FURNACE WITH REGENERATIVE BURNER SWITCHING OPERATION
-
Original Article
-
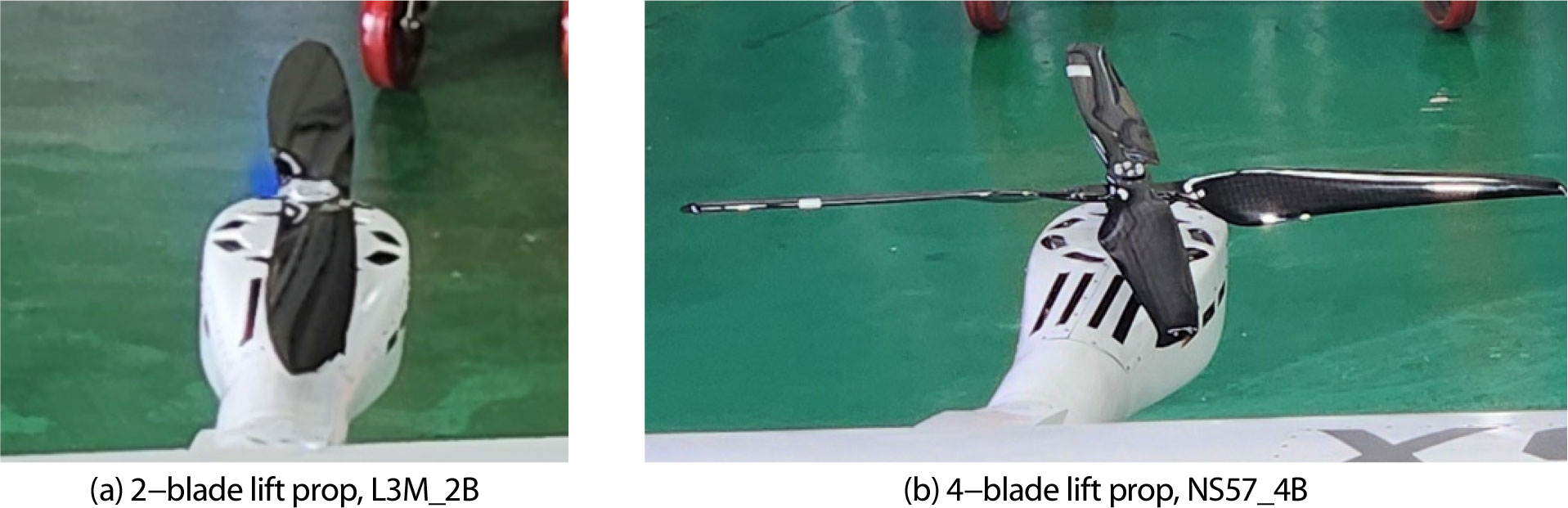
A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON THE AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF 2BLADE AND 4BLADE LIFT PROPS FOR THE OPPAV eVTOL
OPPAV eVTOL에 적용된 2블레이드 및 4블레이드 리프트 프롭의 공기역학적 특성에 대한 비교 연구
-
H.J. Kang
강희정
- In this study, the aerodynamic characteristics of the 2-blade and 4-blade lift props applied to the OPPAV eVTOL were comparatively analyzed using …
- In this study, the aerodynamic characteristics of the 2-blade and 4-blade lift props applied to the OPPAV eVTOL were comparatively analyzed using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) techniques for hover, forward flight, and stationary prop conditions during high-speed forward flight. In terms of hover performance, the Figure of Merit, calculated from power required versus thrust, was generally similar for both props. The unsteady aerodynamic analysis under forward flight conditions clearly confirmed the aerodynamic vibration reduction effect, which was the primary reason for changing the lift prop from 2 blades to 4 blades. The 4-blade lift prop showed a significant reduction in the peak-to-peak amplitude of the vibratory aerodynamic force in the thrust direction compared to the 2-blade prop under all flight conditions. Furthermore, aerodynamic vibrations in the y and z directions of the pod were also identified, caused by the prop's wake and the prop-pod aerodynamic interaction. Frequency analysis also confirmed that the increase in blade count changed the dominant vibratory frequency characteristic from 2/rev to 4/rev. An analysis of the prop drag when the prop was stationary during high-speed forward flight showed that the 2-blade lift prop exhibited minimum drag at a 0-degree blade azimuth angle, whereas the 4-blade lift prop exhibited minimum drag at 45 degrees. These findings suggest that while the 4-blade lift prop is advantageous from a rotational vibration perspective, the 2-blade lift prop may be more favorable for enhancing aircraft performance through stationary drag reduction. - COLLAPSE
-
A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON THE AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF 2BLADE AND 4BLADE LIFT PROPS FOR THE OPPAV eVTOL
-
Original Article
-
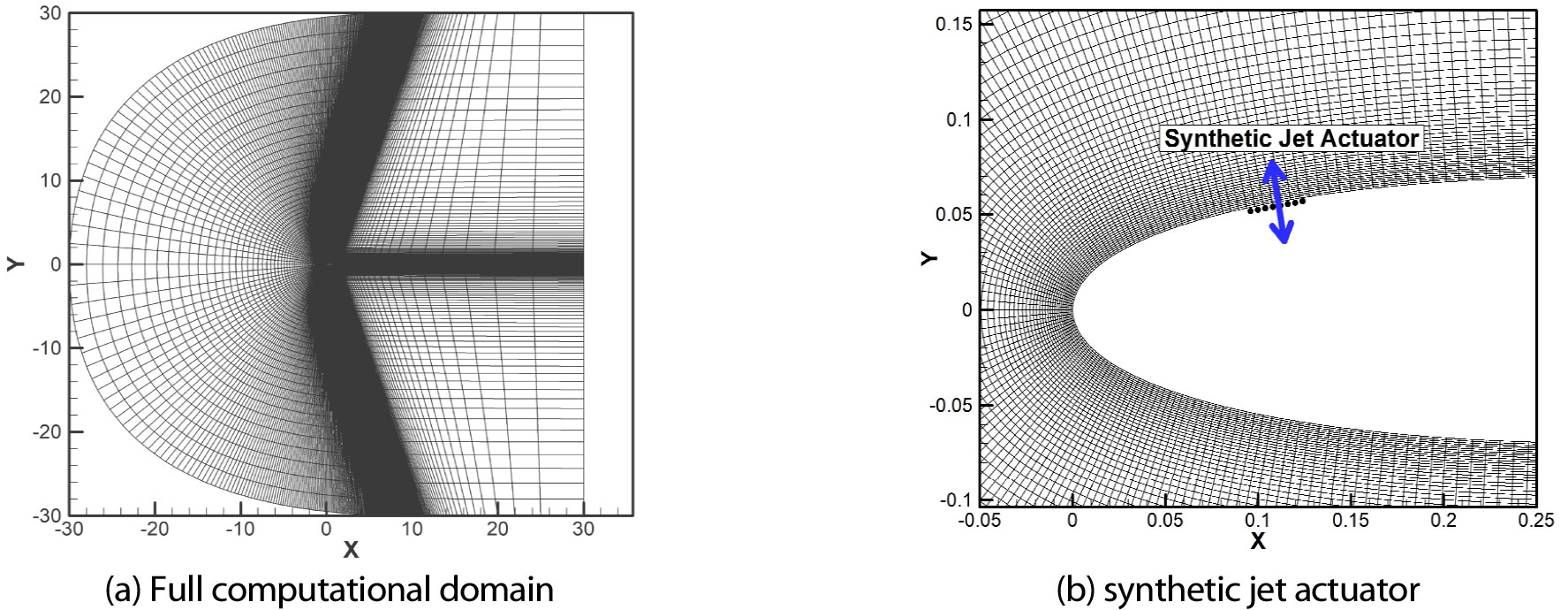
DESIGN OF A POD-LSTM MODEL FOR CLOSED-LOOP CONTROL OF SYNTHETIC JET FLOW
합성제트 유동의 폐루프 제어를 위한 POD-LSTM 모델 설계
-
Y. Son, M.G. Chae, S.H. Park
손예슬, 채민기, 박수형
- An active flow control framework was designed to suppress flow separation and improve aerodynamic performance at high angles of attack. To enable …
- An active flow control framework was designed to suppress flow separation and improve aerodynamic performance at high angles of attack. To enable real-time control of nonlinear unsteady flows, a POD-based reduced-order model was combined with a NARX-LSTM flow estimator. The model predicts dominant flow features from limited pressure-sensor data and reconstructs low-dimensional dynamics efficiently. Sensor optimization was performed through cross-validation to ensure stable and accurate flow reconstruction for the feedback control. Two-dimensional CFD simulations of a NACA0015 airfoil were conducted near stall conditions over a wide range of synthetic jet actuation frequencies. Closed-loop control simulations using a PID controller were performed, and an appropriate range of PID gains was presented to ensure stable and effective actuation response. The results demonstrated that the proposed framework effectively reduced flow separation and thus improved aerodynamic efficiency. This study verifies the capability of data-driven ROM-based surrogate modeling for efficient and accurate active flow control design applicable to future air vehicle systems. - COLLAPSE
-
DESIGN OF A POD-LSTM MODEL FOR CLOSED-LOOP CONTROL OF SYNTHETIC JET FLOW
-
Original Article
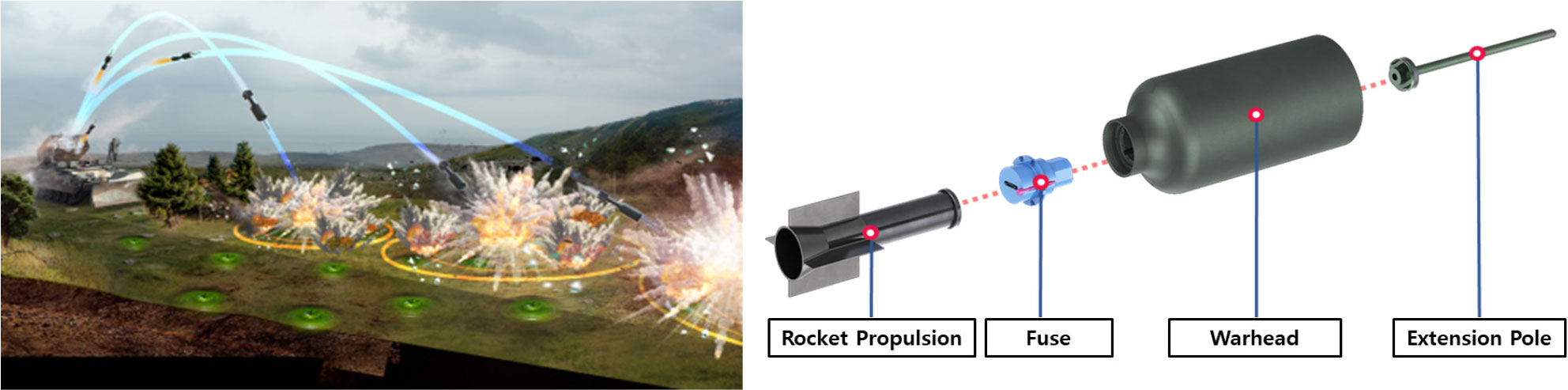
-
A NUMERICAL STUDY ABOUT ASYMMETRIC VORTEX ON ROCKET-LAUNCHED DEMINING PROJECTILE
로켓발사식 지뢰제거탄에 발생되는 비대칭 와류 특성에 관한 수치적 연구
-
H.J. Jung, S.H. Noh, S. Seo, D.N. Joo
정현주, 노성현, 서승표, 주다니
- The Asymmetric Vortex phenomenon, characterized by irregular and asymmetric yaw-inducing flow structures during the flight of rocket-launched demining projectiles, can significantly deteriorate …
- The Asymmetric Vortex phenomenon, characterized by irregular and asymmetric yaw-inducing flow structures during the flight of rocket-launched demining projectiles, can significantly deteriorate flight stability and accuracy. In this study, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) analysis was performed to investigate the aerodynamic mechanism of the Asymmetric Vortex and to propose a design modification to mitigate this flow instability. A series of steady and unsteady simulations were conducted to establish a reliable numerical method. The mesh-density sensitivity was first evaluated using coarse, medium, and fine grids, and the medium mesh was selected as the baseline due to its balance between accuracy and computational efficiency. Subsequently, turbulence-model sensitivity tests were performed using both steady RANS and unsteady URANS/LES approaches. The results showed that the Asymmetric Vortex originates from asymmetric vortex shedding near the projectile’s forebody and shoulder regions. Unsteady simulations successfully captured the time-dependent behavior of the flow, which could not be reproduced in steady analysis. Furthermore, the installation of small fins at 60° intervals around the projectile’s nose was found to reduce the amplitude of the normal-force( C Z ) and pitching-moment( C m ) oscillations, indicating a significant suppression of the Asymmetric Vortex effect. This research provides a systematic CFD framework for predicting and mitigating the Asymmetric Vortex phenomenon and offers valuable insights for the aerodynamic design of rocket-launched demining projectiles to enhance stability and precision. - COLLAPSE
-
A NUMERICAL STUDY ABOUT ASYMMETRIC VORTEX ON ROCKET-LAUNCHED DEMINING PROJECTILE
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Computational Fluids Engineering
Journal of Computational Fluids Engineering
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Computational Fluids Engineering
Journal of Computational Fluids Engineering












