-
Original Article
-
APPLICATION AND COMPARISON OF A VARIATIONAL QUANTUM LINEAR SOLVER USING THE TWO-DIMENSIONAL HEAT EQUATION
2차원 열 방정식에 대한 Variational Quantum Linear Solver의 적용 및 비교
-
S. Kim, D.H. Shin
김선창, 신동혁
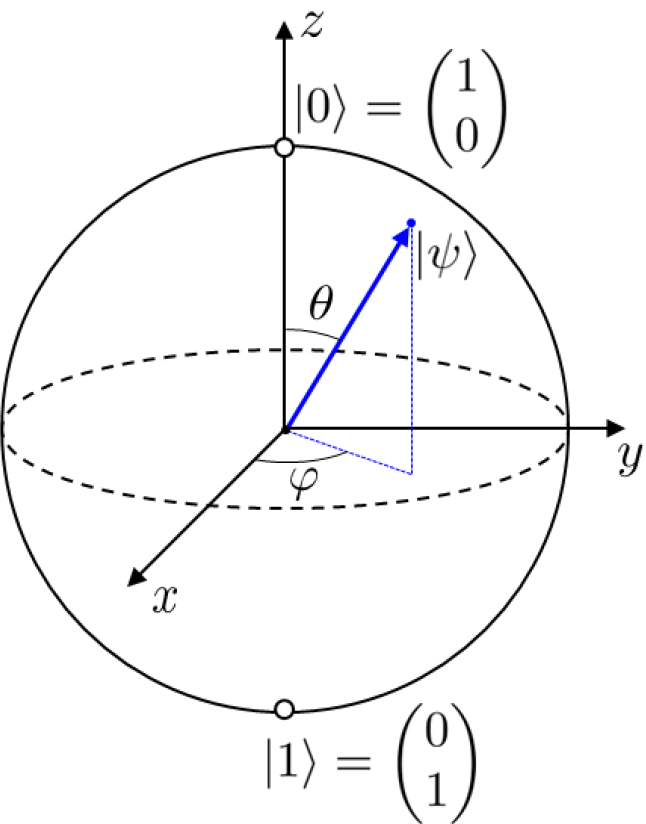
- Quantum computing presents a revolutionary alternative for high-performance computing applications, notably in solving complex problems that are impractical with classical computers. This …
- Quantum computing presents a revolutionary alternative for high-performance computing applications, notably in solving complex problems that are impractical with classical computers. This study employs a variational quantum linear solver (VQLS) to address the two-dimensional steady-state heat equation, demonstrating a potential of quantum algorithms in computational fluid dynamics (CFD). The efficacy of VQLS is tested across three different settings: noiseless emulation, noisy emulation, and quantum hardware, and compared with a classical computing algorithm, the tridiagonal matrix algorithm (TDMA). This comparison illustrates both the current capabilities and the practical challenges faced by quantum computing implementations. This approach highlights remaining hurdles in harnessing quantum computing for real-world scientific and engineering applications. - COLLAPSE
-
APPLICATION AND COMPARISON OF A VARIATIONAL QUANTUM LINEAR SOLVER USING THE TWO-DIMENSIONAL HEAT EQUATION
-
Original Article
-
CONCEPTUAL CALCULATIONS OF CRITICAL FLOWS USING MULTI-SCALE COUPLED THERMAL HYDRAULIC ANALYSIS CODE
다중스케일 연계 열수력 코드를 이용한 임계유동 개념문제 계산
-
I.K. Park, J. Heo
박익규, 허재석
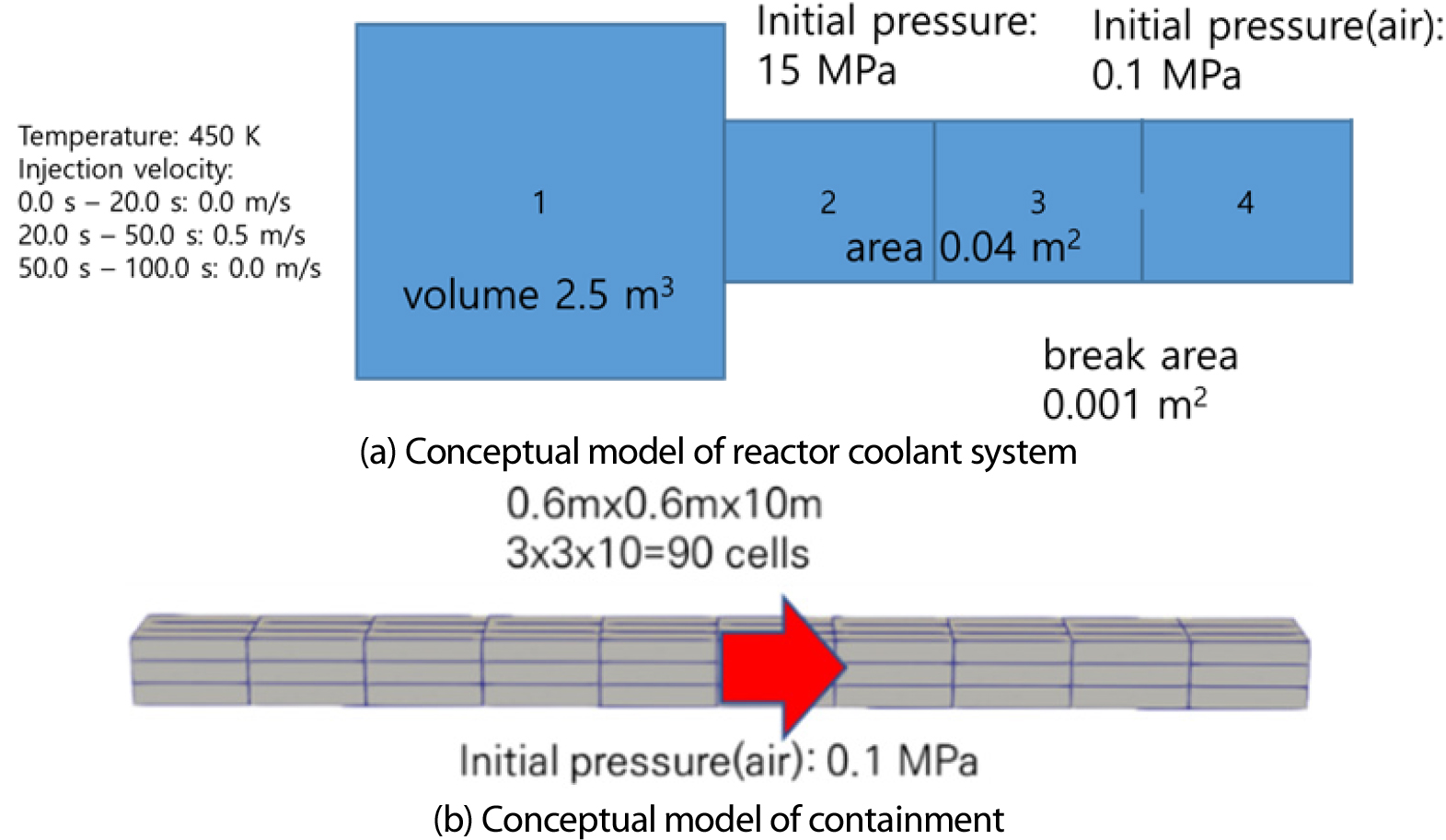
- In this study, the CUPID/SPACE coupled analysis code was validated for predicting critical flow phenomena during a loss of coolant accident, where …
- In this study, the CUPID/SPACE coupled analysis code was validated for predicting critical flow phenomena during a loss of coolant accident, where high pressure reactor coolant vaporizes and is injected into the containment vessel at atmospheric pressure. Thermal hydraulic calculations involving physical models, such as critical flow models, can be effectively performed by system codes. In contrast, three-dimensional behavior analysis can be more suitable for component-scale codes. Therefore, SPACE code was used to calculate the reactor coolant system and the critical flow before and after the break, while the CUPID code was employed to model the mixing of the discharged two phase flow with the containment atmosphere. The boundary conditions in the SPACE code were varied over time to validate the coupled analysis under different critical flow conditions. The results of this study demonstrate that the CUPID/SPACE multi-scale coupled analysis system can physically and accurately calculate critical flow phenomena. - COLLAPSE
-
CONCEPTUAL CALCULATIONS OF CRITICAL FLOWS USING MULTI-SCALE COUPLED THERMAL HYDRAULIC ANALYSIS CODE
-
Original Article
-
DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE INVESTIGATION OF A 3.5MW TWO-STAGE AXIAL STEAM TURBINE
3.5MW급 2단 축류 증기 터빈의 설계에 따른 효율 및 성능 분석
-
S. Tamang, Z. Piao, Y.R. Jung, J.S. Kim, H. Park
사전따망, 박종도, 정예림, 김지수, 박희성
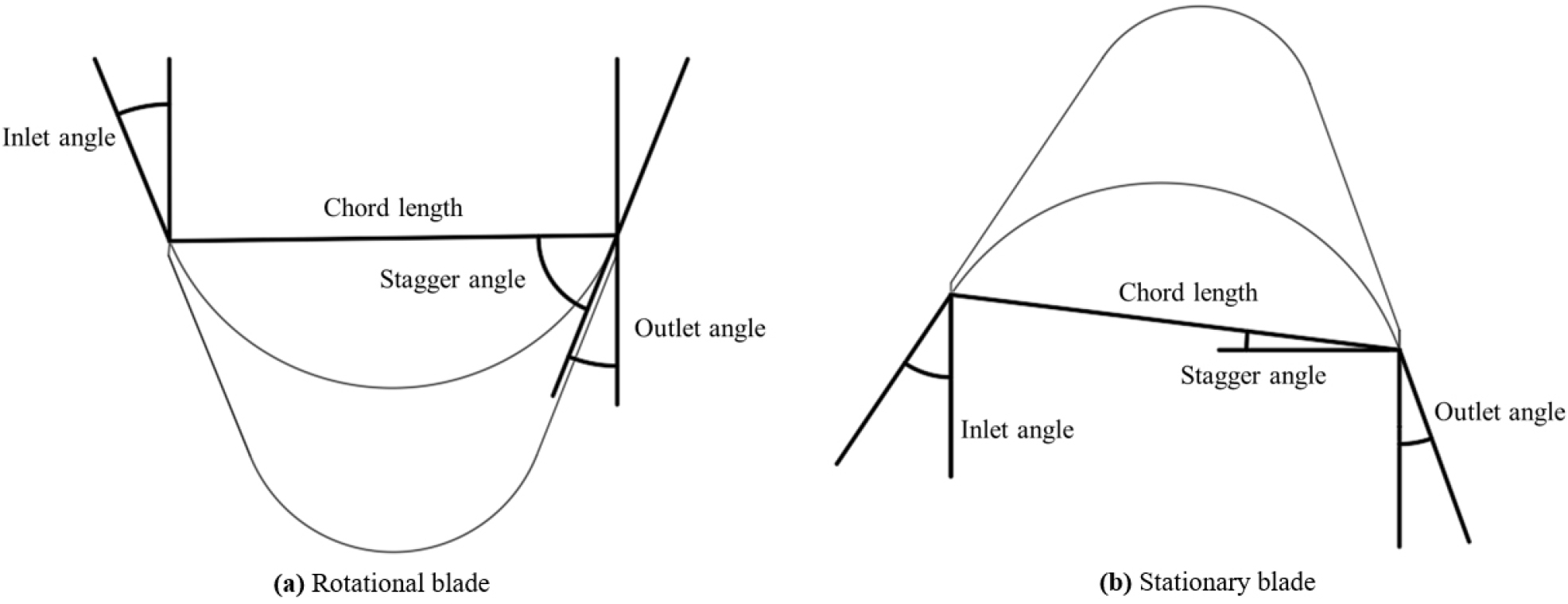
- A steam turbine is a well-known energy conversion device that transforms high pressure steam energy into the mechanical work. This mechanical work …
- A steam turbine is a well-known energy conversion device that transforms high pressure steam energy into the mechanical work. This mechanical work is generally used for electricity generation or to operate mechanical machinery. In this study, we developed the three-dimensional airfoils and flow paths for micro scale axial steam turbine blades adopting both one dimensional and two dimensional design techniques. The steam turbine has been designed with the objective of achieving an output power exceeding 3.5 MW and an efficiency nearly the 50%. The averaged radius of the steam turbine was set at 262.75 mm and the rotational speed of the the blades was targeted at 6000 RPM. The simulation was conducted under varying inlet operating pressure while maintaining a constant temperature. The numerical investigation result indicated that the designed steam turbine achieved a output power of approximately 3.9 MW and an efficiency of 48.45% at an operating pressure of at 47 bar. - COLLAPSE
-
DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE INVESTIGATION OF A 3.5MW TWO-STAGE AXIAL STEAM TURBINE
-
Original Article
-
STUDY ON PROPROTOR AIRFOIL OPTIMIZATION FOR IMPROVING AERODYNAMIC PERFORMANCE OF TILTROTOR AIRCRAFT, PART Ⅰ: AIRFOIL OPTIMIZATION
틸트로터 항공기의 공력 성능 향상을 위한 프롭로터 익형 최적화 연구 Part Ⅰ: 익형 최적화
-
D.H. Kang, D.H. Kim, N.E. Park, J.D. Cho, S.H. Park
강동현, 김두형, 박남은, 조재동, 박수형
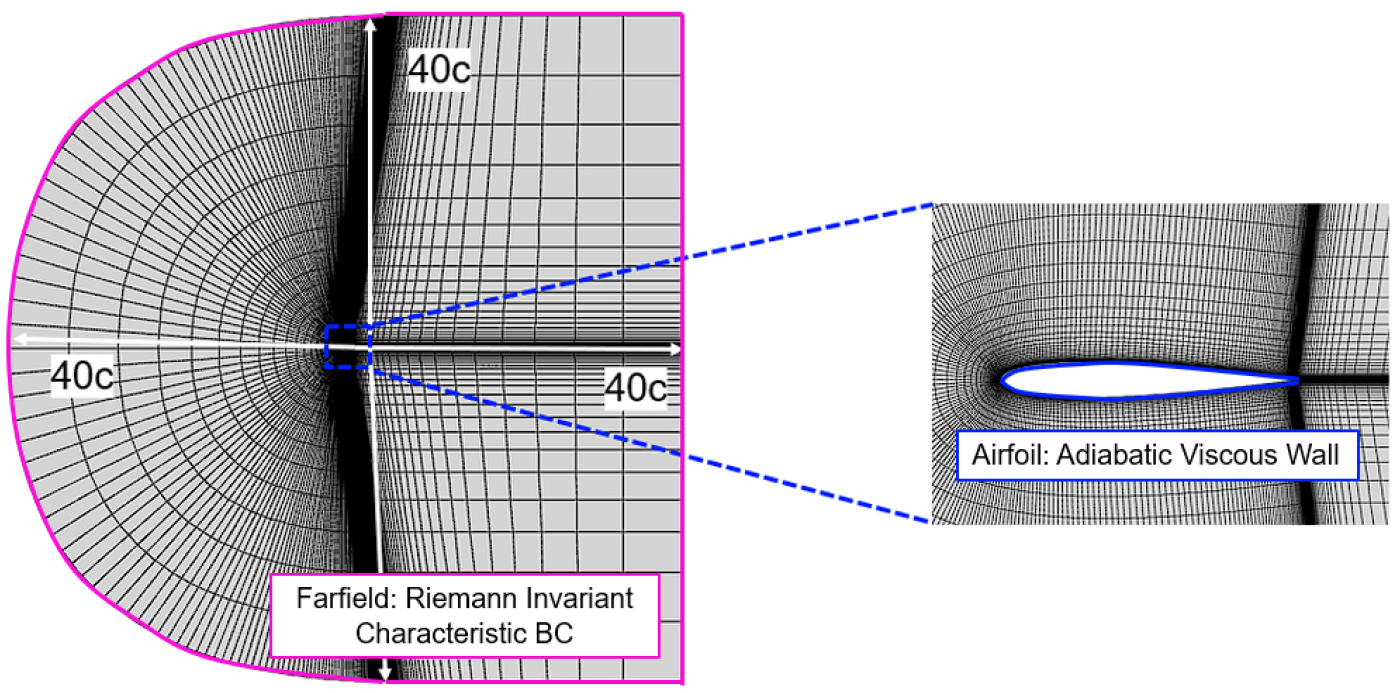
- A computational study on airfoil design optimization of the proprotor for XV-15 tiltrotor aircraft was conducted. The airfoil optimization case of the …
- A computational study on airfoil design optimization of the proprotor for XV-15 tiltrotor aircraft was conducted. The airfoil optimization case of the V-22 Osprey was reviewed and following airfoil design constraints were established: Clmax for maneuver, Cd for cruise, MDD for overspeed, (Cl/Cd)max for hover and Cm0 for structure loads. The base airfoils, NACA 64 series were selected and the shape was deformed using the Hicks-Henne function. A metamodel was generated using response surface method, and a global search was conducted to find candidates. Finally, weight coefficients were applied and optimal airfoils were selected for each section. The optimization results confirmed that optimized airfoils achieve high lift performance and high lift-drag ratio with minimizing drag performance degradation. - COLLAPSE
-
STUDY ON PROPROTOR AIRFOIL OPTIMIZATION FOR IMPROVING AERODYNAMIC PERFORMANCE OF TILTROTOR AIRCRAFT, PART Ⅰ: AIRFOIL OPTIMIZATION
-
Original Article
-
STUDY ON PROPROTOR AIRFOIL OPTIMIZATION FOR IMPROVING AERODYNAMIC PERFORMANCE OF TILTROTOR AIRCRAFT, PART Ⅱ: EVALUATION OF PROPROTOR PERFORMANCE
틸트로터 항공기의 공력 성능 향상을 위한 프롭로터 익형 최적화 연구 Part Ⅱ: 프롭로터 성능 평가
-
D.H. Kang, N.E. Park, J.D. Cho, S.H. Park
강동현, 박남은, 조재동, 박수형
- A computational study was conducted on the XV-15 baseline proprotor and proprotor with the optimized airfoil. Prior to the study, the proprotor …
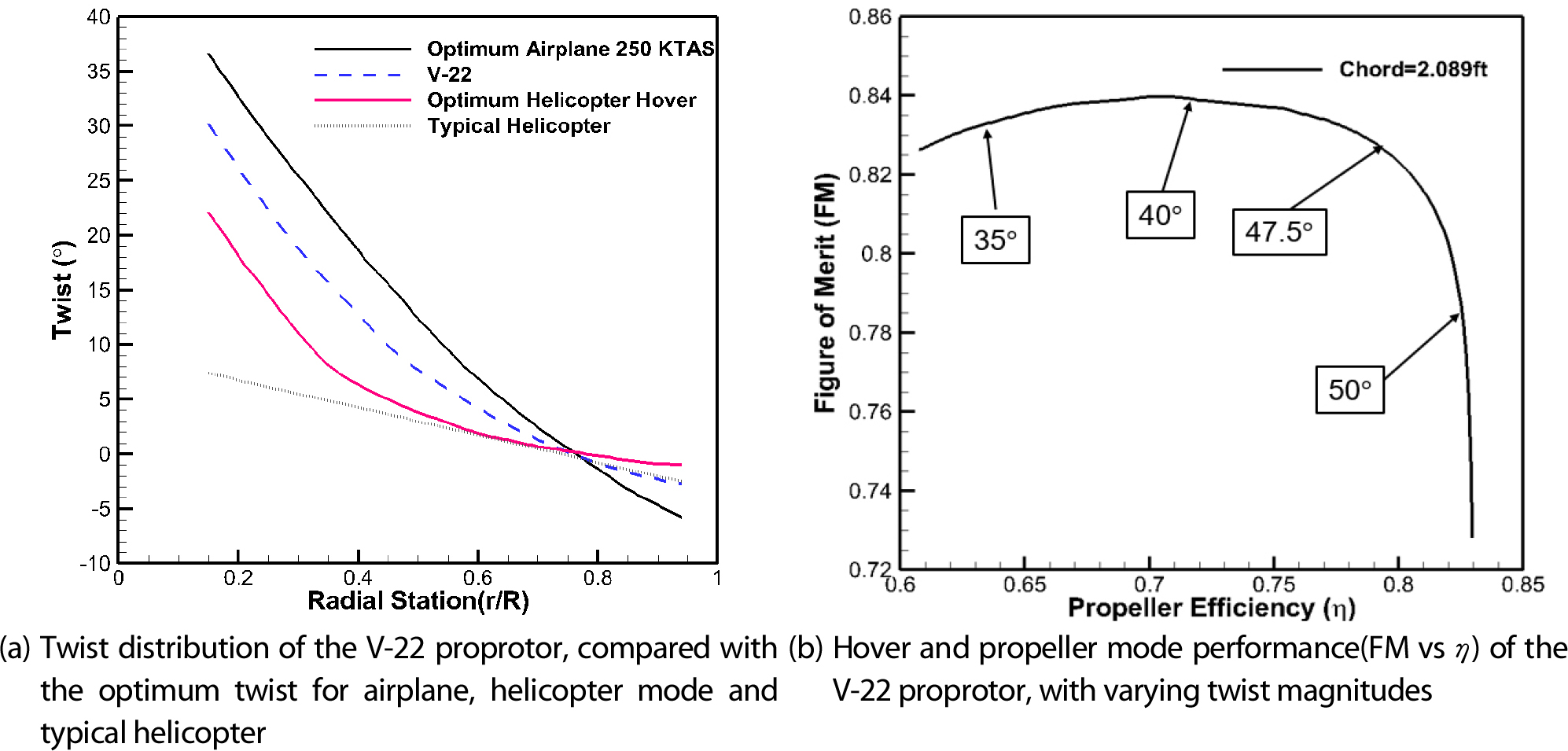
- A computational study was conducted on the XV-15 baseline proprotor and proprotor with the optimized airfoil. Prior to the study, the proprotor design process of the V-22 Osprey was reviewed. The performance coefficients of the XV-15 baseline proprotor and proprotor with optimized airfoil were evaluated under two cases: hover and 300-knot cruise conditions. The same study was conducted with varying the twist magnitude. The analysis results confirmed that there is a design point where both hover and cruise performance were improved compared to the baseline XV-15 proprotor. In the future, this study can be extended by adjusting proprotor planform parameters, such as twist magnitude and taper ratio, to assess their effects on proprotor performance. - COLLAPSE
-
STUDY ON PROPROTOR AIRFOIL OPTIMIZATION FOR IMPROVING AERODYNAMIC PERFORMANCE OF TILTROTOR AIRCRAFT, PART Ⅱ: EVALUATION OF PROPROTOR PERFORMANCE
-
Original Article
-
EFFECTS OF TURBULENCE MODELS ON AIR-GAP FLOW CHARACTERISTICS IN EV MOTOR OIL COOLING SYSTEM
전기차 모터 오일 냉각 시스템의 에어갭 유동 특성에 대한 난류 모델의 영향
-
J. Lee, J. Kim, G. Shin, J. Lee, S. Choi, K. Kim, S. Kang
이준희, 김재홍, 신건, 이정우, 최세현, 김기태, 강성원
- As efficient thermal management is essential for high-speed electric vehicle (EV) motors, accurate prediction of oil cooling inside motor air-gap has become …
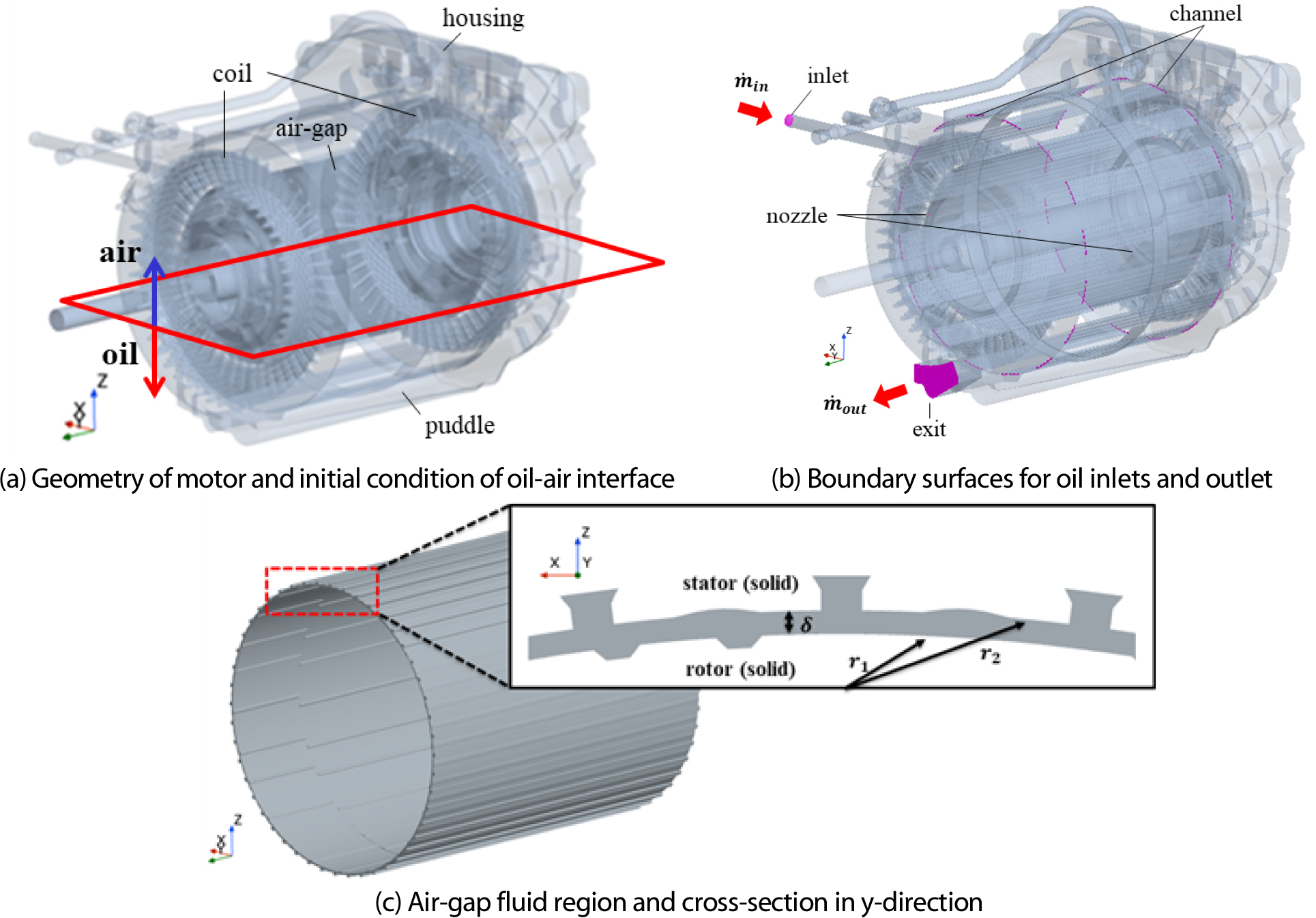
- As efficient thermal management is essential for high-speed electric vehicle (EV) motors, accurate prediction of oil cooling inside motor air-gap has become very important. This study aims at analyzing the flow and thermal characteristics in the air-gap region and comparing the results using the Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) and large eddy simulation (LES) approaches. In the air-gap region, it is found that the LES case underpredicts the Taylor vortex cell size and oil mass compared to the RANS case while overpredicting flow mixing, which leads to a relatively higher heat transfer rate and lower friction loss. The observed high sensitivity of the mechanical and thermal indices to the turbulence models motivates proper selection of the turbulence model for accurate prediction of the characteristics in the air-gap region. - COLLAPSE
-
EFFECTS OF TURBULENCE MODELS ON AIR-GAP FLOW CHARACTERISTICS IN EV MOTOR OIL COOLING SYSTEM
-
Original Article
-
A STUDY ON THE COOLING OF WATER-COOLED LITHIUM-ION BATTERIES FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES BASED ON VARIATIONS IN INLET AND FLOW PATH GEOMETRY
유입구 및 유로 형상 변화에 따른 전기자동차용 수냉식 리튬 이온 배터리 냉각에 관한 연구
-
E.J. Kim, J.M. Park, H.S. Yang, J.H. Jang, J.H. You, Y.H. Sung
김의종, 박지민, 양학수, 장주현, 유지호, 성열훈
- As electric vehicle(EV) adoption increases, the need for efficient energy storage solutions, such as lithium-ion batteries(LIBs), also grows. However, higher battery capacities …
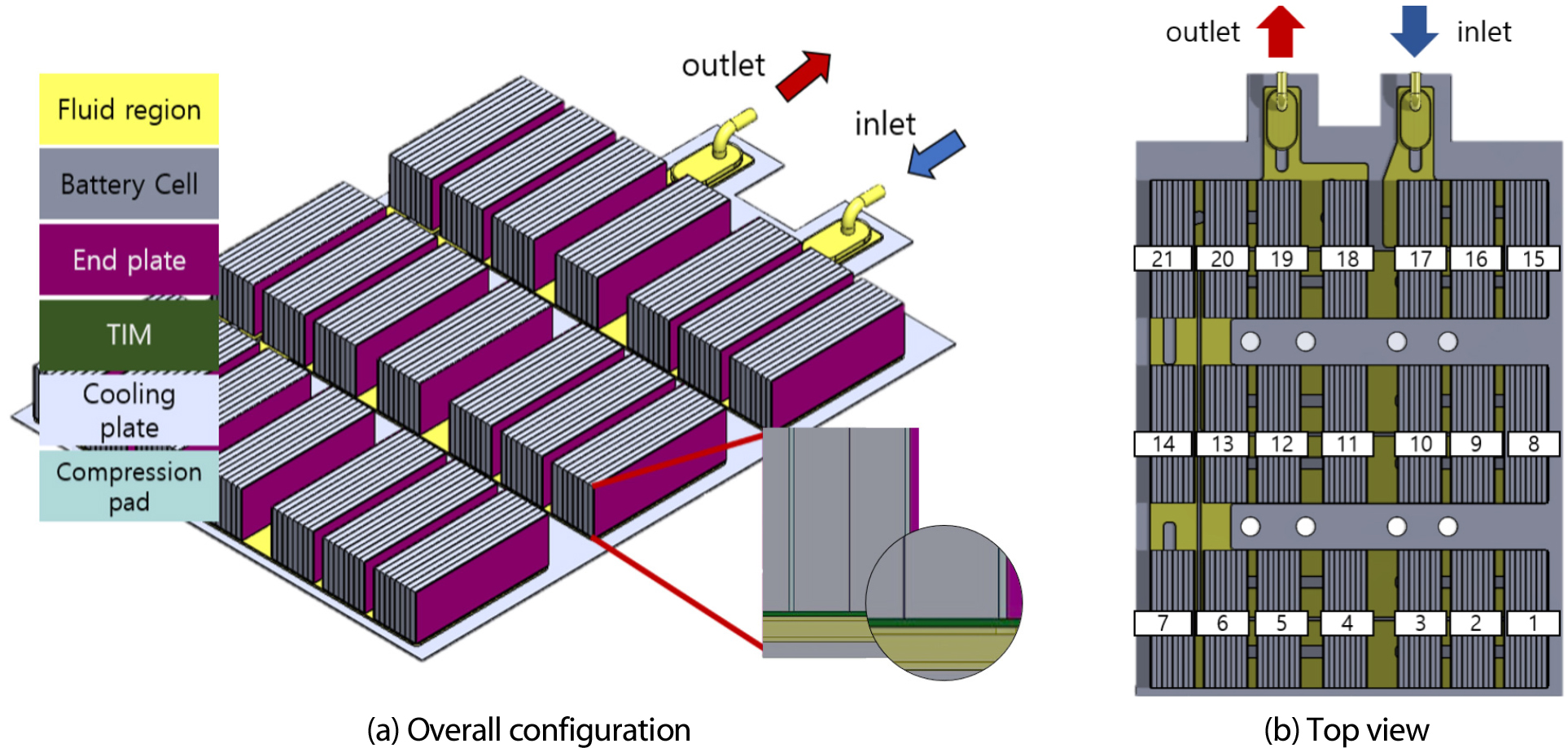
- As electric vehicle(EV) adoption increases, the need for efficient energy storage solutions, such as lithium-ion batteries(LIBs), also grows. However, higher battery capacities bring a higher risk of thermal runaway, impacting safety and performance. Effective thermal management is crucial for ensuring reliability and longevity. This study focuses on improving the performance of the water-cooling system for LIBs by modifying its geometry. Various designs, such as vortex generators(VG) and curved channels(CC), are tested to enhance heat transfer and cooling efficiency. These changes aim to achieve uniform heat distribution, reducing temperature differences between battery cells and preventing thermal runaway. Using computational fluid dynamics(CFD) simulations, the impact of different nozzle shapes and flow paths on thermal management is analyzed. The results show notable improvements in cooling performance and temperature uniformity that could enhance both safety and battery lifespan. - COLLAPSE
-
A STUDY ON THE COOLING OF WATER-COOLED LITHIUM-ION BATTERIES FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES BASED ON VARIATIONS IN INLET AND FLOW PATH GEOMETRY
-
Original Article
-
ANALYSIS OF HUB EFFECT ON LIFT OFFSET COAXIAL ROTOR USING CFD-TRIM COUPLED ANALYSIS METHOD
CFD-Trim 연계 해석 기법을 이용한 리프트 오프셋 동축반전 로터의 허브 효과 분석
-
M.H. Cho, S.H. Hong, D. Park, S.H. Park, K.W. Cho
조민형, 홍성현, 박다운, 박수형, 조금원
- In this study, the effect of the hub on a high-speed lift-offset coaxial rotor is analyzed using KFLOW, an in-house code developed …
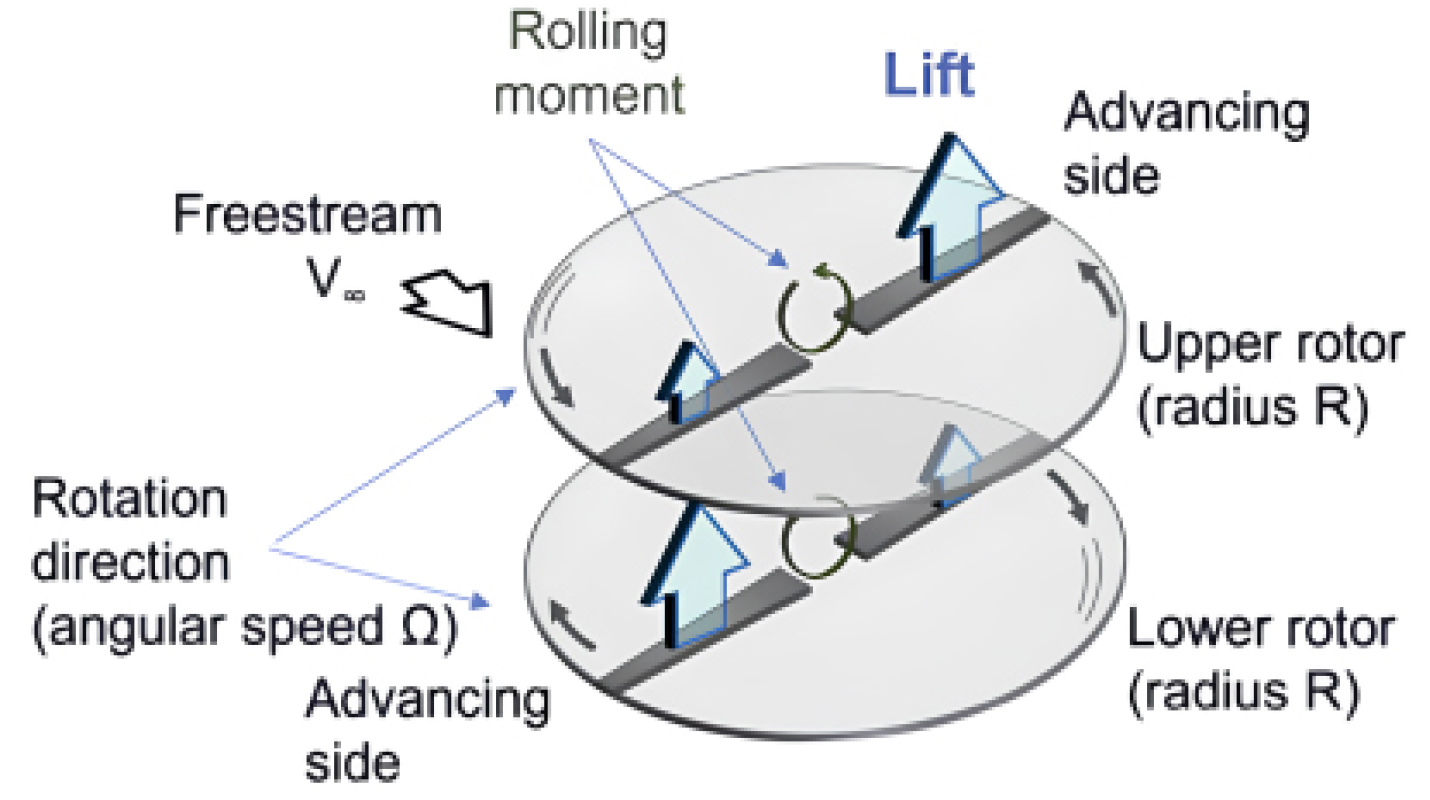
- In this study, the effect of the hub on a high-speed lift-offset coaxial rotor is analyzed using KFLOW, an in-house code developed at Konkuk University. To investigate the hub effect at forward flight speeds of 150 knots and 200 knots, trim is performed under lift-offset conditions, and a CFD-Trim coupled analysis is conducted using CAMRAD II as the trim code. This approach reduced computational costs while ensuring high-accuracy trim results. At both 150 knots and 200 knots, the trim variable results exhibited similar trends regardless of the presence of the hub. Due to this similarity, the sectional normal force distributions were nearly identical in the azimuth range of 30° to 360°. However, differences is observed in the azimuth range of 0° to 30°. In the lower rotor, additional peaks appeared, or the peak magnitudes increased due to the influence of the downwash induced by the rotor when the hub was considered. Furthermore, in the upper rotor, the root-induced BVI(Blade-Vortex Interaction) exhibited different characteristics depending on the presence of the hub. When the hub was absent, the vortices generated at the root directly influenced the blades passing near the azimuthal angle of 10° without interacting with the hub. In contrast, when the hub was present, the root-generated vortices interacted with the hub before affecting the blades. Considering the hub better reflects the actual physical phenomena, and it is essential to include the hub in CFD analysis of coaxial rotor in forward flight. - COLLAPSE
-
ANALYSIS OF HUB EFFECT ON LIFT OFFSET COAXIAL ROTOR USING CFD-TRIM COUPLED ANALYSIS METHOD
-
Original Article
-
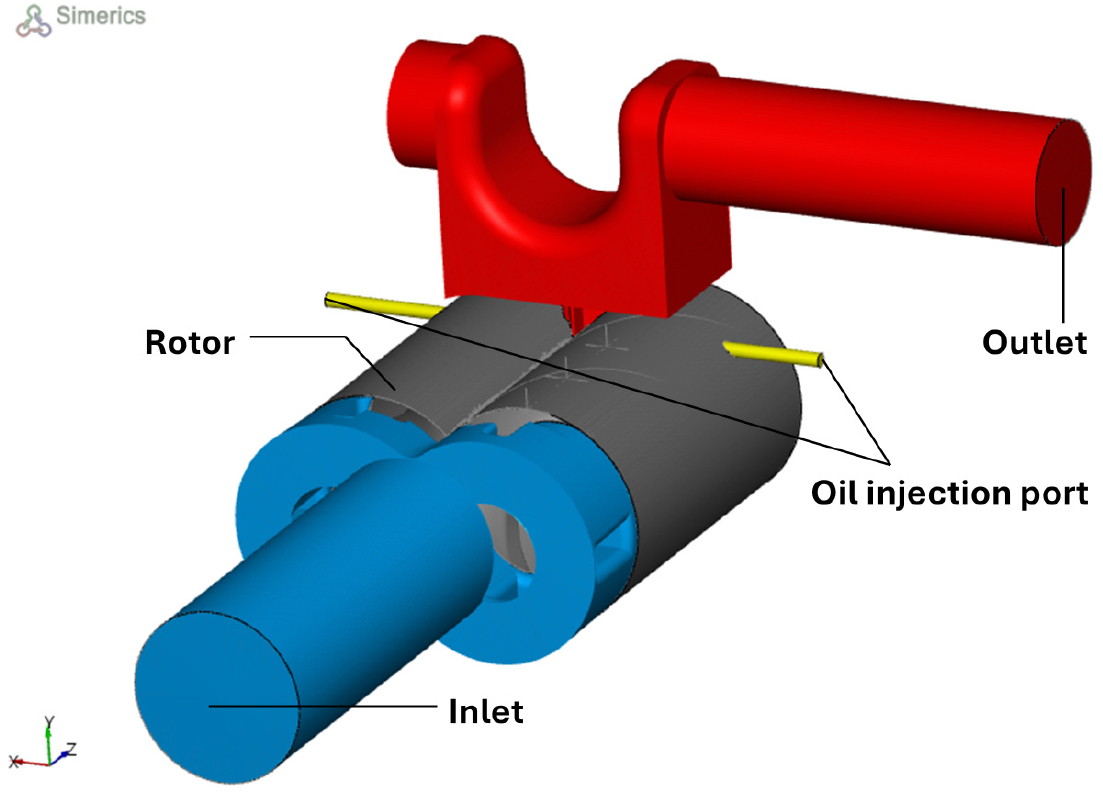
NUMERICAL STUDY OF ROTOR CLEARANCE AND OIL INJECTION FLOW EFFECTS IN A SCREW COMPRESSOR
로터 간격 및 오일 유량을 고려한 스크류 압축기의 수치적 연구
-
M. Kim, G. Son
김민준, 손기헌
- This study numerically investigates the effects of rotor clearance and oil injection on the thermal-fluid characteristics of screw compressors using SimericsMP+. The …
- This study numerically investigates the effects of rotor clearance and oil injection on the thermal-fluid characteristics of screw compressors using SimericsMP+. The oil flow within the compressor is modeled using the Volume-of-Fluid (VOF) method, treating air as an ideal gas and oil as an incompressible fluid. Simulations are conducted with a deforming grid and standard k-ε turbulence model. The computational model is validated against reference data obtained under oil-free condition. Subsequently, a parametric study on rotor clearance and oil injection rate is conducted to analyze their influence on compressor performance and to identify optimal operating conditions. - COLLAPSE
-
NUMERICAL STUDY OF ROTOR CLEARANCE AND OIL INJECTION FLOW EFFECTS IN A SCREW COMPRESSOR
-
Original Article
-
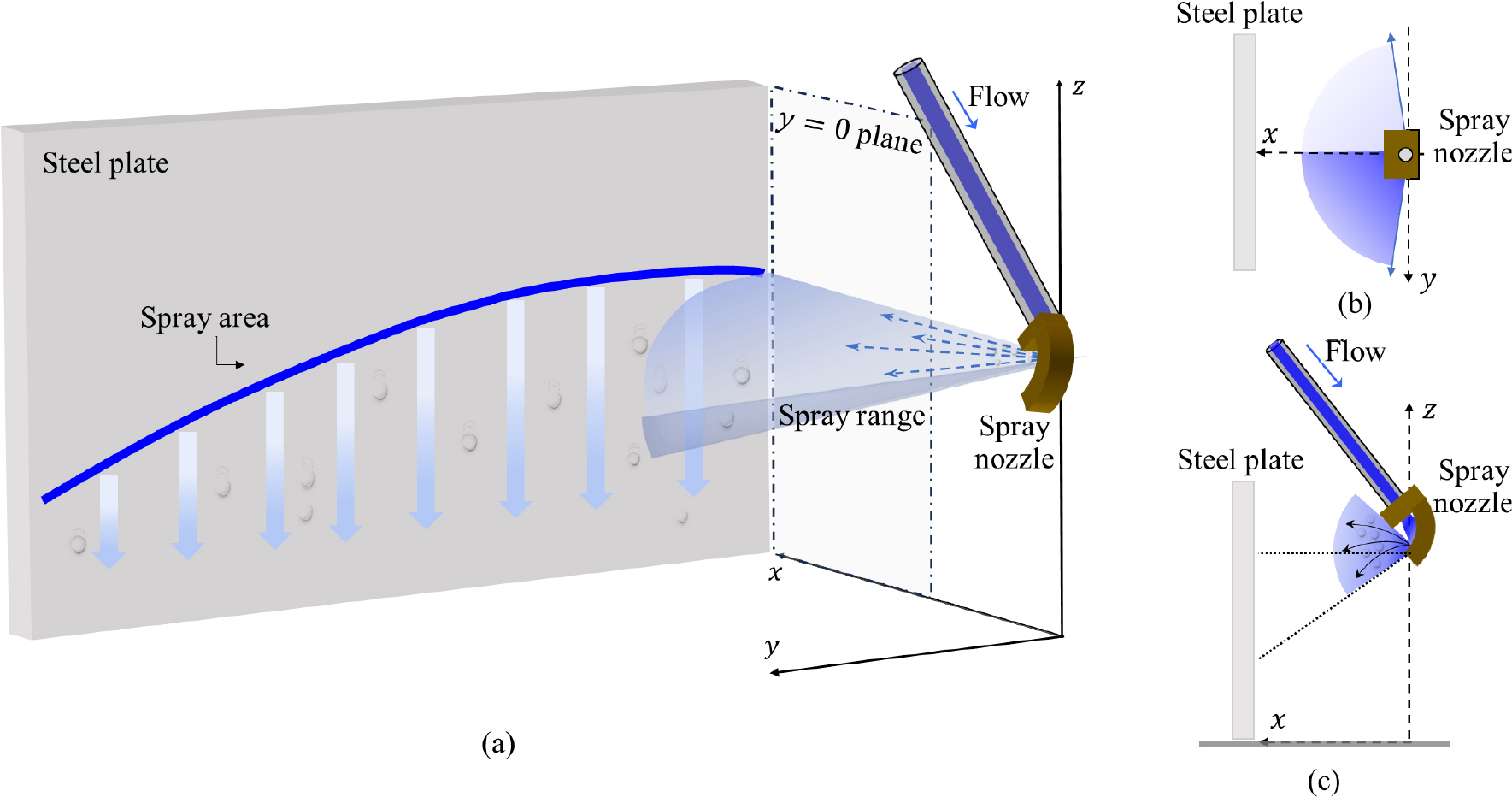
CODE DEVELOPMENT FOR ESTIMATING THE COOLING EFFECT OF A STEEL PLATE USING SURFACE FILM MODEL
표면 액막 모델을 이용한 강판 냉각 효과 추정을 위한 코드 개발
-
W. Lee, I.D. Suh, I. Lee, H. Kim, J. Lee, S.H. Rhee
이원강, 서인덕, 이인수, 김현승, 이재봉, 이신형
- In the present study, a CFD code was developed to estimate the cooling effect of a seawater supply system on a steel …
- In the present study, a CFD code was developed to estimate the cooling effect of a seawater supply system on a steel plate. The seawater supply system was modeled using nozzle spray characteristics and experimental data, with the seawater being sprayed in a fan-shaped pattern. To calculate the flow of the film on a steel plate, surface film model was employed. Conjugate heat transfer model was used to develop a CFD code for calculating the heat transfer between the seawater and the steel plate without boiling effects. Calculating the trajectory of the sprayed fluid particles in the atmosphere is computationally expensive, so the estimated spray area data from mathematical modeling was used in the computational analysis. Gravity and drag force acting on the fluid particles were considered to estimate the spray area. The fluid particles were assumed to be spherical shape, constant size, with no break-up. The estimated spray area data are used in the calculations of the source terms in the governing equations to compute surface film flow. We performed a quasi-steady analysis by adding the source terms at specific intervals. The cooling effect of the seawater supply system on the steel plate was estimated for various nozzle angles and flow rates, and the spray area and effective cooling area were calculated. The wetted area on the steel plate surface was defined as the spray area, while the effective cooling area was defined as the region where the steel plate surface temperature drops below 300 K after 600 seconds of seawater spraying. The spray area and effective cooling area all increased as the flow rate increased. Considering the wind and ship velocity, the spray area and effective cooling area decreased significantly compared to the case without wind and ship velocity. - COLLAPSE
-
CODE DEVELOPMENT FOR ESTIMATING THE COOLING EFFECT OF A STEEL PLATE USING SURFACE FILM MODEL
-
Original Article
-
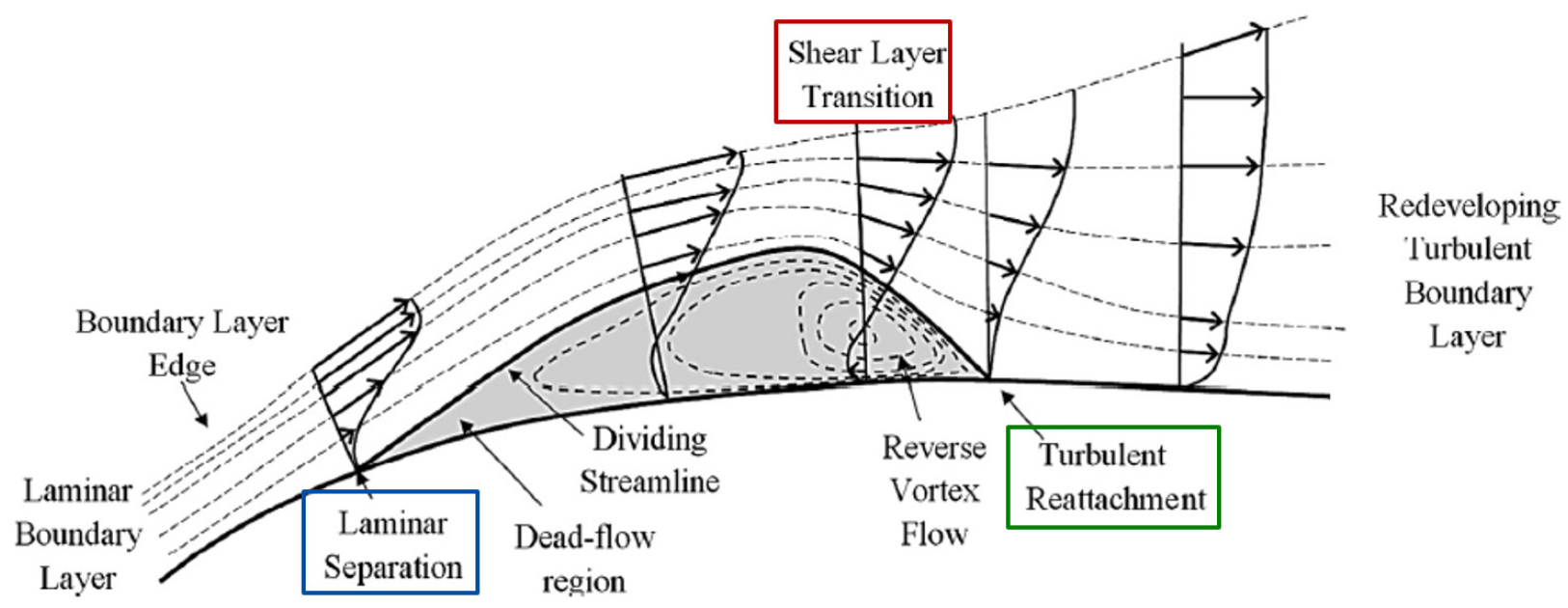
LARGE EDDY SIMULATION ON DAE-51 AIRFOIL FLOW AT LOW REYNOLDS NUMBER CONDITIONS
저 레이놀즈수 조건의 DAE-51 익형 유동에 대한 대와류모사
-
D. Park
박동훈
- A large eddy simulation (LES) has been performed to examine the flow over a DAE-51 airfoil at low Reynolds number conditions (less …
- A large eddy simulation (LES) has been performed to examine the flow over a DAE-51 airfoil at low Reynolds number conditions (less than 105). A grid dependency test was conducted to validate the reliability of the results and validate the feasibility of LES with the commercial code. The characteristics of the flow field were examined in detail, including the formation of a laminar separation bubble (LSB) and transition process at chosen angle of attack and Reynolds number. Criteria were established to identify laminar separation, transition onset, and reattachment points based on the mean shear stress along the airfoil surface. The variations in separation, transition onset, and reattachment points with changes in angle of attack and Reynolds number were investigated, and their impact on aerodynamic performance were evaluated. The position and length of LSB were found to significantly affect the distribution of pressure and skin friction coefficients on the airfoil surface, thereby influencing aerodynamic coefficients. Under low Reynolds number conditions, the formation, position, and length of LSB vary significantly with angle of attack, which complicates the drag polar pattern. As the Reynolds number decreases, the separation bubble or separated region lengthens, resulting in a substantial deterioration in the lift-to-drag ratio due to a significant increase in pressure drag. - COLLAPSE
-
LARGE EDDY SIMULATION ON DAE-51 AIRFOIL FLOW AT LOW REYNOLDS NUMBER CONDITIONS
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Computational Fluids Engineering
Journal of Computational Fluids Engineering
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Computational Fluids Engineering
Journal of Computational Fluids Engineering












